Same details on DIM Configuration
(private networks, machines with multiple network interfaces,
etc.)
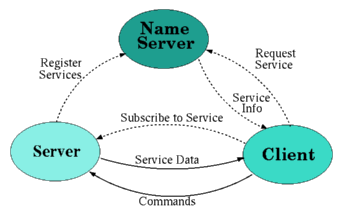
Setting Up DIM Processes
A few environment variables can be used to configure DIM processes:
- DIM_DNS_NODE
Before starting a Server or a Client to tell them where the DNS is running.
- DIM_DNS_PORT
Before starting the DNS, a Server or a Client if the default DNS port number
(2505) is not to be used.
For example in order to be able to run two DNSs in the same machine.
- DIM_HOST_NODE
Before starting a Server, to specify which IP name/IP address should be used
by clients to connect to this server
(if the default host interface* is not to be used).
It can be the IP name (ex.: pclhcb155.cern.ch) or the IP address (ex.:
137.138.214.208)
* The default host interface can be retrieved with the command line command:
hostname
- Note: The DIM Name Server (DNS) is also a Server (DIS_DNS) for
replying to DID and for answering DimBrowser requests.
So DIM_HOST_NODE can also be set for the DNS in order to choose on which
interface it should answer.
Some DIM functions can also be used to dynamically Set Up DIM
Processes:
- For a DIM Client:
- For a DIM Server:
These functions can be used to independently specify which DNS to use
for Servers and Clients even if both parts are running in the same
process (but need to use different DNSs).
Note: The "obsolescent" functions dim_set_dns_node(),
dim_set_dns_port(), etc. specify the same DNS for a complete process (so
for both client and server part if running in the same process).
Using DIM across different Networks
In
a node with two Ethernet interfaces (or in general visible on two networks):
- The DNS will answer to servers and client on both networks. Only its
server part - DIS_DNS (the one that answers to DID and DimBrowser
requests) would in principle answer only to one of the networks (either
the default interface* or the one specified via "DIM_HOST_NODE").
- But, in fact, if the DNS or any server is started with the
environment variable DIM_HOST_NODE set to the interface that is not the
default* one. Than both the DNS (including the server part) and any DIM
servers running on this dual interface machine will be accessible from
both networks. For example DID will work fine on both networks.
* The command "hostname" returns the name of the default network
interface.
Note: Although the DNS may respond to all servers and clients on both
networks, of course clients on one network will not be able to connect
to servers which have a single interface on a different network.
A program: DimBridge is available, as an example, to transfer
DIM services and commands from one DNS to another. (Supposing that the
two DNSs are on different networks). Please note that such a Bridge
should be used with care as it could create a bottleneck, since all
services and commands have to be "tunneled" via it.
Usage: DimBridge [from_node] to_node services
from_node - by default DIM_DNS_NODE
to_node - the complete node name of
the new DNS
services - the list of service names
(wildcards allowed)
The user can also create its own client/server program that is a
client on one interface and a server on the other one, using the same
DNS, but then the user has to guarantee that the Service names published
by the Server part are different from the ones already available. (DIM
does not allow multiple services with the same name using the same DNS).
Port Numbers used by DIM
When setting
up (private) networks and gateways you may need to know the port numbers
used by DIM for example to configure Firewalls.
- The DNS responds by default on port 2505 (although this can be
changed by the variable DIM_DNS_PORT).
- DIM Servers (including DIS_DNS the server part of the DNS) will
use ports in the range 5100 to 6000. A DIM server on one PC will
take the first free port in this range, a second server on the same
PC will take the next free port, etc.

